Hackathon Tracks

Agriculture
The agricultural sector faces a wide range of challenges affecting food production and sustainability, especially in Asir. Climate changes significantly impact crop availability, rainfall, soil fertility, and the exposure of crops to pests and diseases, disrupting stable food supplies and food security. Managing water resources is another major challenge, as over-extraction for irrigation leads to groundwater depletion. There is a critical need for solutions and techniques that improve irrigation efficiency and agricultural practices that consume less water. Additionally, urban and industrial expansion encroaches on agricultural lands, increasing desertification, reducing vegetation, and affecting the climate, necessitating a balance between agricultural needs and environmental conservation efforts.
Examples of Challenges:
- Using high-performance computing to create AI models that increase crop productivity and reduce pest infestations.
- Designing smart irrigation systems that optimize water use through real-time data analysis.
- Developing precision agriculture tools to improve farm management practices.


Natural Resources
Natural resources are materials that occur naturally within the environment and can be used for economic gain or to support life. They are usually categorized into renewable resources, such as solar, wind, hydropower, and biomass, and non-renewable resources like fossil fuels and minerals. Issues related to natural resources include overexploitation, leading to depletion, and pollution of air, water, and soil from industrial and agricultural activities and improper waste disposal. The Asir region faces deforestation, loss of soil fertility, soil salinization, and water scarcity, impacting its agricultural productivity.
Examples of Challenges:
- Predicting resource usage trends and depletion to aid in management and conservation efforts.
- Monitoring deforestation and water bodies to provide data for immediate action to prevent resource depletion.
- Improving resource use efficiency in agriculture, water distribution, and energy consumption to reduce waste and enhance efficiency.
- Detecting pollution sources and levels through sensors and data analysis for timely interventions to reduce pollution.
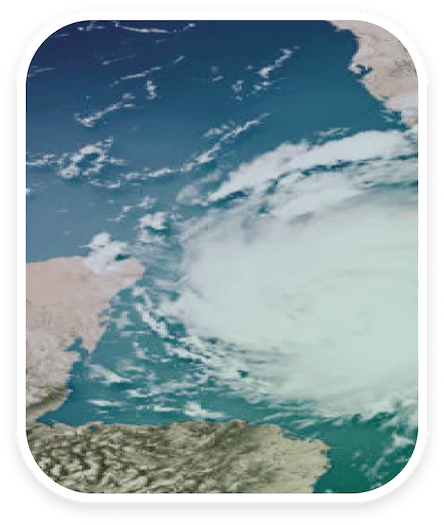
Climate
Climate change refers to long-term changes in temperatures and weather patterns over extended periods. While these changes can be natural, human activities are now the main driver of climate change. Burning coal, oil, and gas releases carbon dioxide and other gases, affecting the climate. Deforestation reduces the ability of nature to regulate greenhouse gas levels, and industrial and agricultural waste generation produces gases that affect the atmosphere. Sudden temperature and rainfall changes lead to increased flooding in some areas, droughts in others, polar ice melting, and sea level rise. Climate change increases the frequency and severity of hurricanes, floods, and wildfires and disrupts weather patterns, causing crop failures, food shortages, and impacts on livestock.
Examples of Challenges:
- Improving weather and climate forecasts for better planning against extreme weather conditions.
- Monitoring greenhouse gas emissions and identifying actions needed to reduce them.
- Enhancing agricultural efficiency through the analysis of weather, soil, and plant data to boost crop productivity and reduce waste.
- Predicting sandstorms and severe climate changes.